CRM Types
Whether you’re in sales, marketing or customer service, a CRM is critical to the success of your business. It acts as the internal system of record and single point of truth for the company.
Research by Salesforce shows that CRM applications can help increase sales by up to 29%, sales productivity by up to 34% and sales forecast accuracy by 42%.
A CRM lets you establish and cultivate long-term relationships with your customers so that you can increase revenue, profitability, and customer satisfaction.
But which type of CRM do you need? Which is best for your business?
CRMs make up the largest software category – estimated to reach $35B by 2023 – with thousands of vendors catering to different industries, company sizes and sales team structures.
Across the categories, three main types of CRM emerge:
- Operational
- Analytical
- Collaborative
So it’s important to know which type is best for your business.
In this article, you’ll discover more about each type of CRM, what each one offers, how you can use them in your business, and why they should not be viewed as a silver bullet.
What is a CRM?
A CRM – short for Customer Relationship Management – is a software solution that helps businesses to capture prospect and customer interactions in a single database.
In 2008, only 12% of businesses used a cloud-based CRM – this figure has now increased to 87%!
Research by Innoppl Technologies showed that 65% of sales reps who adopted a mobile CRM solution hit sales quota. Only 22% of reps using a CRM without the mobile functionality hit the same sales targets.
Teams can use the information in a CRM to send emails, make calls, add notes, schedule appointments, create reports, and manage sales pipelines from the CRM system. Any interactions from the customer are automatically added to their record, so everyone has the latest visibility.
Who Uses a CRM?
Sales teams can use a CRM to learn more about their prospects and customers, and manage their sales pipeline better. The CRM also helps automate day-to-day tasks, like scheduling follow-up calls at an agreed interval. And managers can track, view, and report on their team’s performance.
Editor’s note: Different sales team structures – inside vs outside vs channel – have very different needs and should not take the same approach to customer relationship management. For example, a field sales CRM should look, feel and act a lot different than an inside sales CRM. The type of CRM should always match the business model. The risk is lower end-user adoption. In fact, over 90% of companies have a CRM adoption rate less than 40%. And the #1 reason for lack of CRM adoption – manual data entry. |
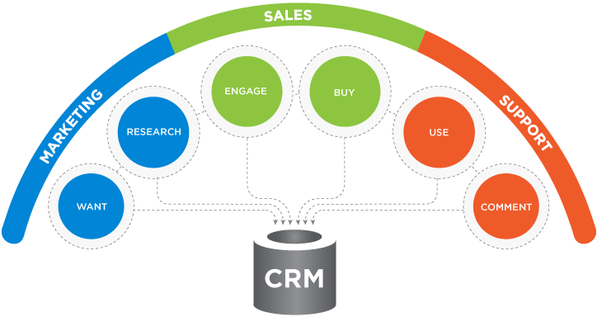
Marketing teams can use a CRM to target their ideal customer profiles (demographics, location, etc.) when planning campaigns. The CRM also measures the ROI on their marketing activities and campaigns so they can adjust accordingly in the future.
Customer service teams can use a CRM to help maintain and retain existing customers. The CRM database provides insights into a customer’s previous issues and interactions, so they can manage the current situation and plan future customer engagement activities.
The Core Benefits of a CRM
A CRM solution allows you to focus on selling and keeping your customers happy.
But there are other benefits, too, like enhancing customer relationships, reducing customer churn rate, increasing sales and revenue, and automating communication and tasks.
Let’s take a look:
Enhance customer relationships
Research by Software Advice shows that 74% of users said their CRM system gave them improved access to customer data.
A CRM captures every interaction along the customer journey (prospect to lead to customer) from multiple teams to create a 360 degree view of the customer. Using this information enables you to provide better customer service and communication across all departments.
Reduce data entry
A CRM reduces the mundane data entry tasks by automatically adding and updating customer records in the database. For example, when a potential customer visits your website or signs up for your mailing list, or when existing customers send an email, their information is automatically loaded into your CRM.
Improve communication
With every piece of customer information in one place, you can ensure everyone across the business is communicating the right message consistently.
Visualize pipelines
A CRM helps to visualize your sales pipelines so you can prioritize which deals to work on. By visualizing the pipeline, managers can create conversion percentage benchmarks and immediately see when deals are falling through the cracks.
Reduce churn rate
Research by Capterra shows that CRM users reported their CRM had a significant impact on customer retention.
Using data from the CRM – e.g. user requirements, preferences, buying habits, etc. – you can customize and personalize your products and services to help reduce churn rate.
Increase revenue
Insights from a CRM help you identify your most profitable customers and build stronger relationships with them. This inside knowledge increases your sales revenue as you know the optimal time to target repeat business.
With a deep understanding of the ideal customer profile, you can create “lookalike” accounts when prospecting. For example, once you know who your most valuable clients are, and where they are located, you can formulate more targeted marketing and field sales campaigns.
Collaboration
Without a CRM, business functions often work in silos with separate pieces of customer data. A CRM shared across business functions means you can work together to achieve the same goals and objectives.
Editor’s note: We’ve looked at the core benefits of a CRM solution, but the application and use cases will vary depending on the specific needs of the team using it. In the next section, we’ll cover the 3 main types of CRM tools, and focus in on the sales team use cases for each different type. |
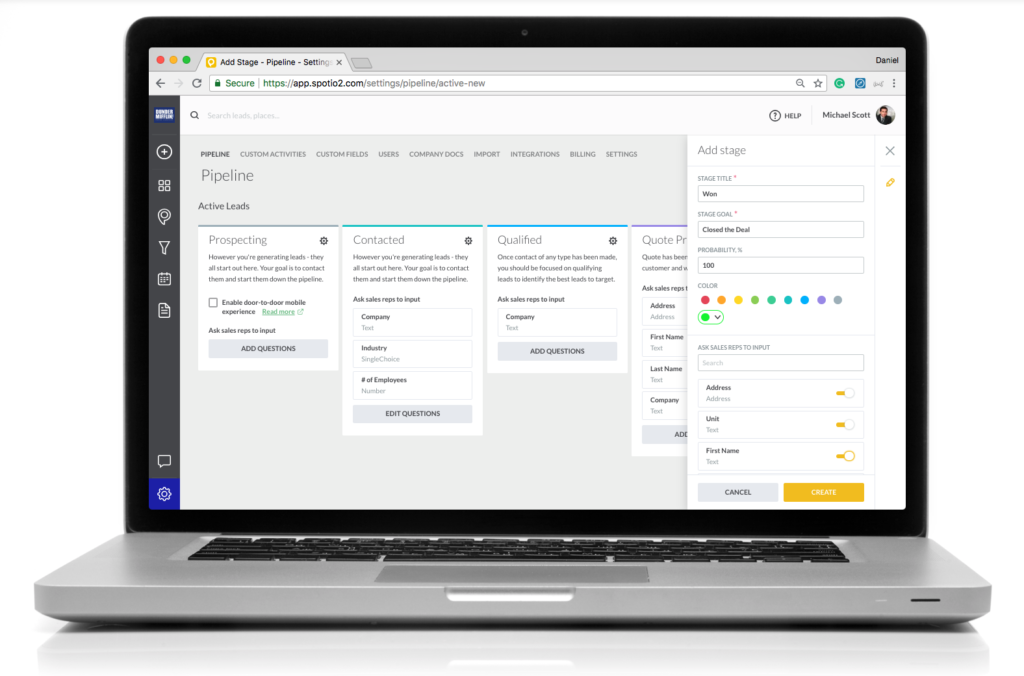
3 Main Types of a CRM
There are three main types of CRM systems:
- Operational
- Analytical
- Collaborative
Let’s take a look:
#1 – Operational CRM
An Operational CRM is the most common type of CRM and is used in many different industries.
This type of CRM is excellent for handling customer-facing communications and helping businesses manage their day-to-day sales, marketing, and customer service operations.
Sales automation
An Operational CRM can automate your sales process from lead generation to closing sale, as well as managing your sales force. For example:
Scheduling follow-up reminders to contact prospects at agreed intervals.
Tracking a contact and updating their status from prospect to qualified lead once they’ve completed certain actions or met specific criteria.
Reporting on sales team performance.
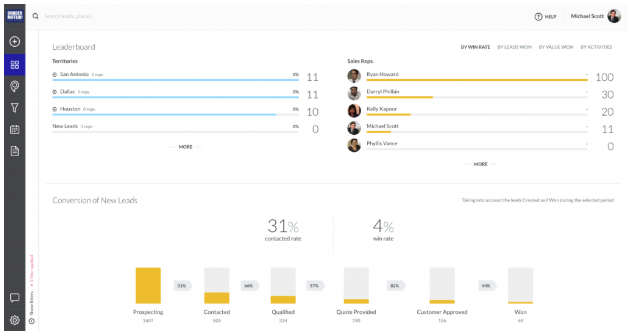
Field sales example:
SPOTIO’s CRM helps Field Sales Reps build and visualize their pipeline with its lead management module. Reps can filter leads, opportunities, and customers with colorized pins to visualize their pipeline:
Inside sales example:
Salesforce offers a variety of CRM categories, including Marketing Cloud, Service Cloud, Analytics Cloud, App Cloud, and Sales Cloud with functionality best suited for larger inside sales teams.
Inside sales reps can use the Sales Cloud CRM to manage contacts, access sales enablement documents, track sales activity – leads, opportunities and closed deals – and take action from any location, on any device.
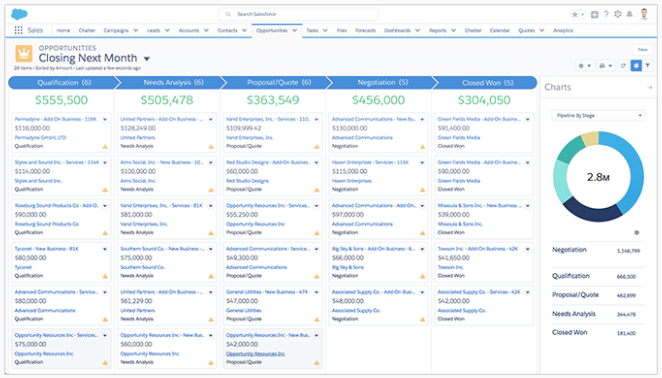
The CRM allows reps to spend more time selling to the right prospects, and do it with the best data at their fingertips.
Editor’s note: It’s important to remember that one size does not fit all. For instance, an early stage inside sales software company should be using a different CRM than an enterprise outside sales team. Similarly, many companies have both outside and inside sales teams. In this situation, it’s better to have one primary CRM and then “bolt-on” a mobile technology built specifically for the needs of the field sales teams. For example, large enterprise sales teams often use Salesforce for its core internal sales activities and then bolt on SPOTIO for its field sales reps, as both tools work together seamlessly. SPOTIO’s native 2-way integration with Salesforce makes it easy for reps to collect data and record notes in the field then sync it back into Salesforce in real-time. See how Salient Medical Solutions bolted SPOTIO’s mobile CRM functionality on top of Salesforce and increased field sales productivity by over 15%. |
Marketing automation
An Operational CRM also allows you to automate some of your marketing activities at various stages of the customer funnel. For example:
– Adding and tagging new email subscribers to your CRM automatically.
– Initiating a welcome email campaign whenever a new prospect enters the system.
– Identifying existing leads in your CRM for your next marketing campaign.
HubSpot allows you to automate your email campaigns using targeted workflows, and then personalize your emails for each recipient using specific details from your CRM:
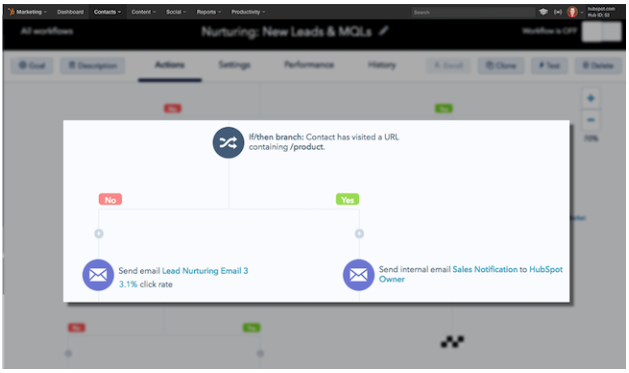
Key Features
- Stores and organizes contact and lead information
- Streamlines daily business operations
- Automates some sales and marketing activities
You should consider an operational CRM if:
- You have a linear sales process
- You are a sales and marketing led business (new business focused)
- You lean towards workflow automation and prefer software to perform redundant administrative tasks
#2 – Analytical CRM
An Analytical CRM gathers, stores, and analyzes information about your customers. This typically includes customer data, marketing data, sales data, and service data.
Here’s how each of them dovetails together.
Customer data includes general details like location, age, gender, marital status, and income bracket. The more data you gather, the clearer picture you create; e.g. What does this person want? What are their buying habits? These reports help you plan your marketing campaigns.
The SPOTIO Lead Machine is a great time-saver when you want to generate qualified leads in a chosen territory. Using up-to-date customer profile data you can find prospects who are ready to buy in three quick steps:
- Select your target area
- Create your ideal customer profile (e.g. income, credit capacity, age of home, eco friendly, square footage, etc.)
- Import your leads and start selling
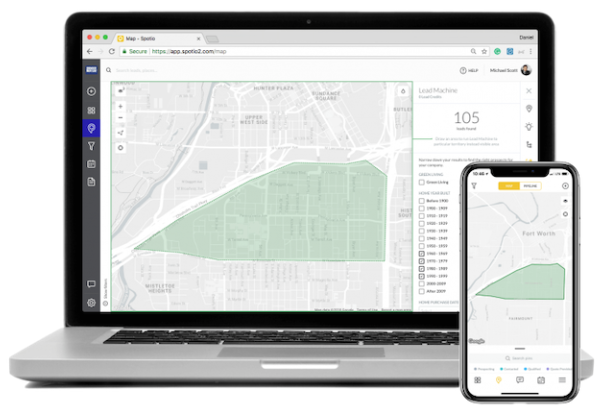
Marketing data lets you measure the success of your campaigns. For example, you can generate reports to discover which leads convert the best and which campaigns yield the highest ROI.
Sales data, along with marketing and customer data, help you plan new campaigns, assign sales territories and track rep performance. Reports can help identify sales trends and patterns. So, for example, you can understand:
- Which products are your Top Sellers
- Which products sell least in Winter
- Which products sell most in Florida
- Which reps sell the most
- Which territories should be assigned to different reps
Service data helps with three core areas:
- Customer service
- Customer satisfaction
- Employee performance
Customer service
Your staff has access to data in the CRM which includes buying habits and past purchases, so when they’re dealing with a customer, they can quickly check for up-sell or cross-sell opportunities.
Customer satisfaction
An analytical CRM system allows you to capture and address customer satisfaction issues early on. For example, if customers complain about the same thing; e.g. a software bug, you’ll be able to see the pattern and issue a quick fix to stop any further escalation.
Employee performance
As well as tracking customer complaints, an analytical CRM can also track how your employees are handling those complaints, plus other customer interactions in general. These reports help identify areas for improvement in performance reviews.
For example, SPOTIO gives managers a clear view of how the top sales reps are performing and also where leads are falling off in the sales process:
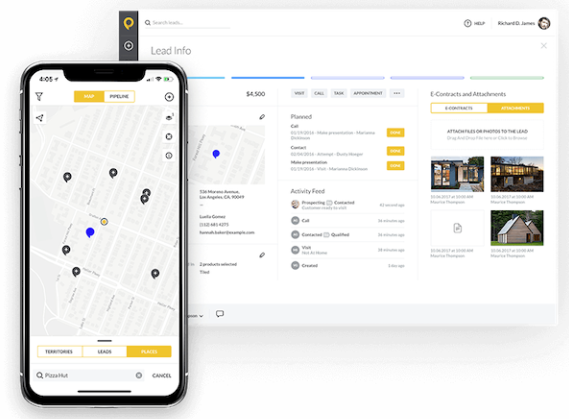
Historical data shows exactly what happened with every prospect up to the point of the last contact. The background knowledge saved within SPOTIO prepares the sales reps for their next customer meeting and helps sales managers coach their team to success:
Key Features
- Gathers, stores, and analyzes customer information from multiple teams.
- Helps organizations to plan sales and marketing campaigns.
- Tracks key performance indicators set by the business.
You should consider an analytical CRM if:
- You have account management driven sales process
- You have a finance led management style
- Your end-users are data driven and value metrics
#3 – Collaborative CRM
A Collaborative CRM – sometimes called a Strategic CRM – enables an organization to collect, organize, and share customer information across multiple teams.
For example, sales and purchase history, customer service contact, marketing preferences, and technical support interaction.
When teams collaborate and share customer information, they can maximize profitability, and increase customer satisfaction and loyalty.
There are two significant parts to a Collaborative CRM:
- Interaction management
- Channel management
Interaction management allows you to record and analyze every interaction a customer has with your company. Monitoring interactions helps you identify issues that an individual or groups of customers may be experiencing.
Channel management allows you to record the preferred method of communication for each of your customers. Some customers prefer text messages, others prefer a phone call, and some might prefer email.
Either way, it’s better to contact your customers using their preferred method, so you get a positive response.
For example:
Imagine your company sells a mobile app. A Collaborative CRM would allow multiple teams to resolve issues reported by customers.
The customer service team can get an overall view to see how many customers are experiencing the same problem with your app.
If it’s a widespread problem, they can alert the technical support team and request a quick fix to alleviate the situation. Then, when the fix is ready, the customer service team can contact each customer using their preferred communication channel to advise them of the next steps.
Furthermore, this information can be shared with the marketing team so they can tailor messages in the future.
The integrated e-Contract functionality in SPOTIO gives sales reps immediate access to office files and documents. Instead of emailing documents back and forth, customers can sign contracts on the spot:
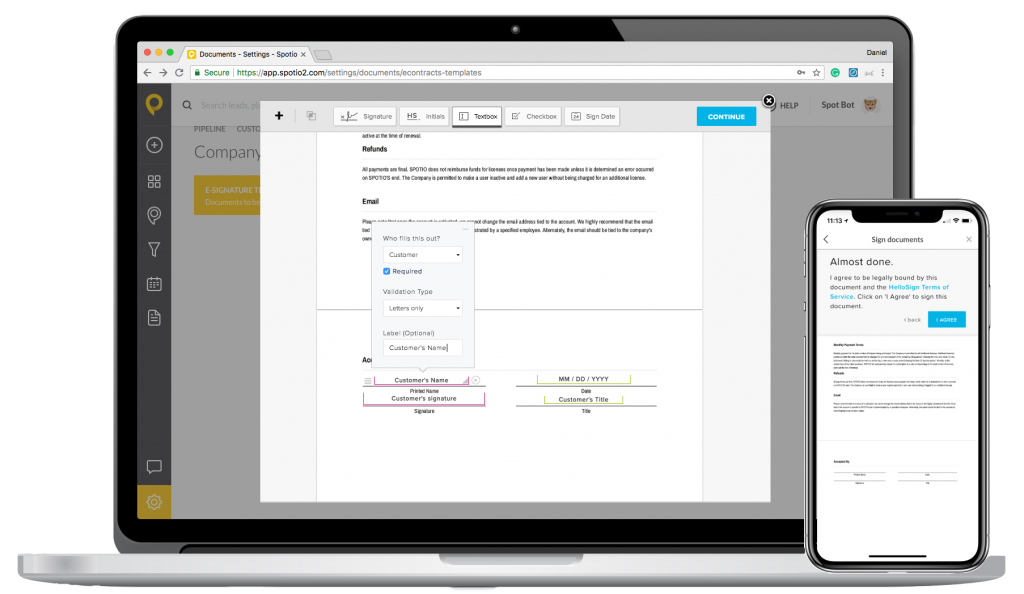
Reps can also take pictures onsite as well as access files, such as product spec sheets, presentations, etc.
Key Features
- Collects, organizes, and shares customer data across multiple teams
- Improves the overall customer experience with unified messaging
- Increases customer satisfaction and loyalty
You should consider a collaborative CRM if:
- You have multiple stakeholders and departments moving in and out of the platform
- You have multiple locations or have a digitally driven company culture where most communication occurs online
- Your comfortable with customer data being easily accessible by most in the company
Accelerate Your Pipeline With Customer Relationship Management
So, what type of CRM does your business need?
Here’s a quick recap:
An Operational CRM is excellent for handling customer-facing communications as it helps businesses manage their daily sales, marketing, and customer service operations.
An Analytical CRM is best for getting an overall picture of your sales, marketing, and service performance as it gathers, stores, and analyzes customer information from multiple teams.
A Collaborative CRM is best for connecting multiple teams and improving customer loyalty, as it gives a 360-degree view of the customer journey from prospect to customer support.
All that said, a CRM is not a silver bullet. Rather it is a foundational cornerstone of your sales tech-stack, and companies that are achieving the most success – whether operational, analytical or collaborative – recognize this.
A CRM will only take your sales, marketing and customer support so far, and oftentimes you’ll need to purchase additional software to integrate with a CRM as your team evolves and business grows.
Outside sales teams looking for an all-in-one CRM solution that accommodates operational, analytical and collaborative use cases should try a demo of SPOTIO’s field sales CRM today!
______
Questions or comments? Contact SPOTIO at [email protected] or comment below.
SPOTIO is the #1 field sales acceleration and performance management software that will increase revenue, maximize profitability, and boost sales productivity.
Want to see a product demonstration? Click here to see how SPOTIO can take your sales game to the next level.



